Understanding H-Shaped Inductor: Design, Applications, and Benefits
Inductors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, playing a crucial role in energy storage, filtering, and signal processing. Among various inductor designs, the H-shaped inductor stands out due to its unique structure and performance advantages. This article explores the design principles, applications, and benefits of H-shaped inductors while providing practical insights for engineers and hobbyists.
What Is an H-Shaped Inductor?
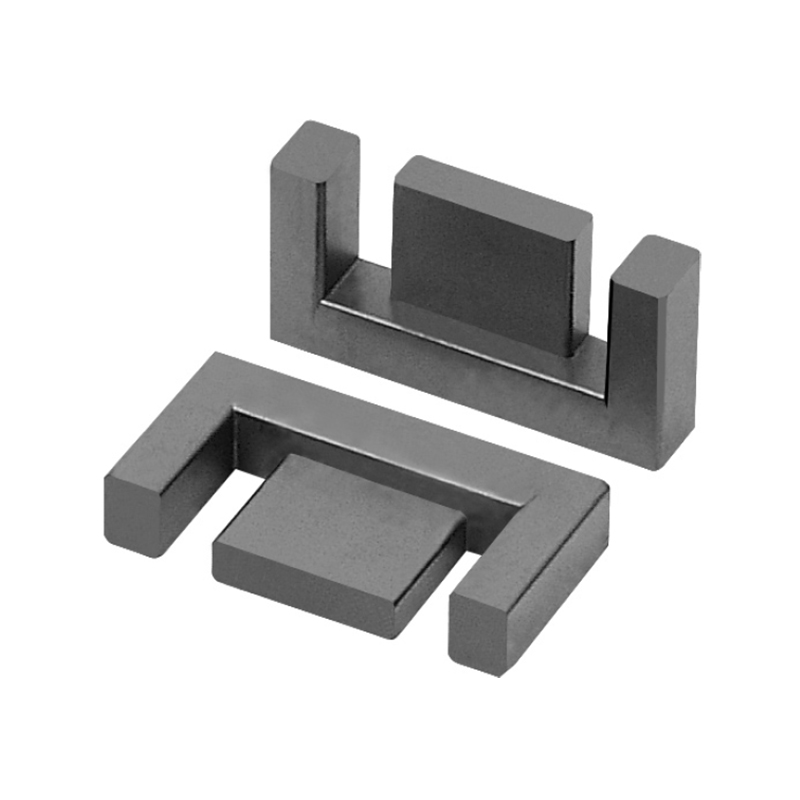
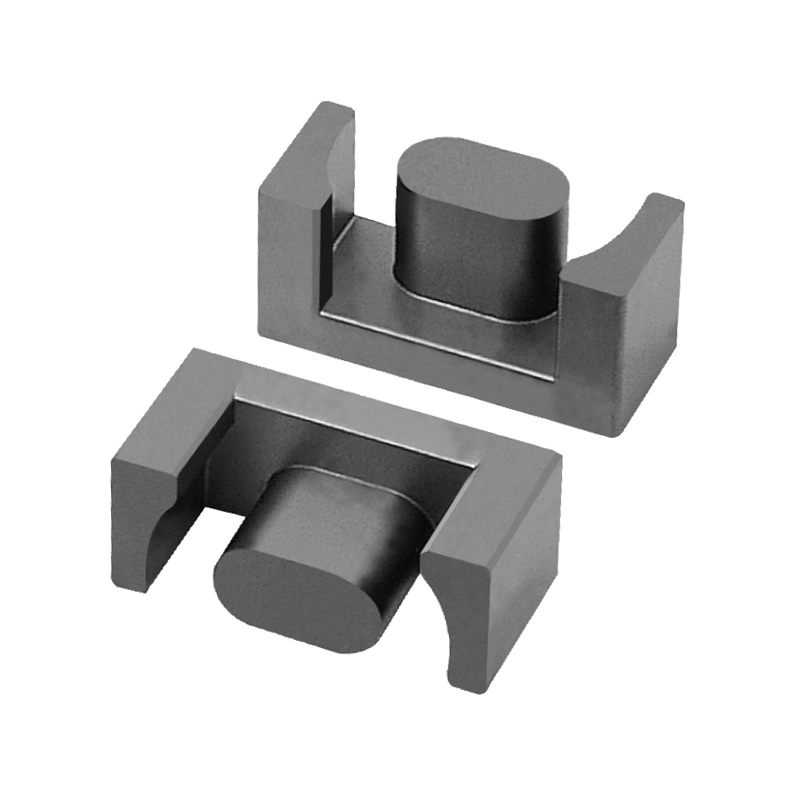
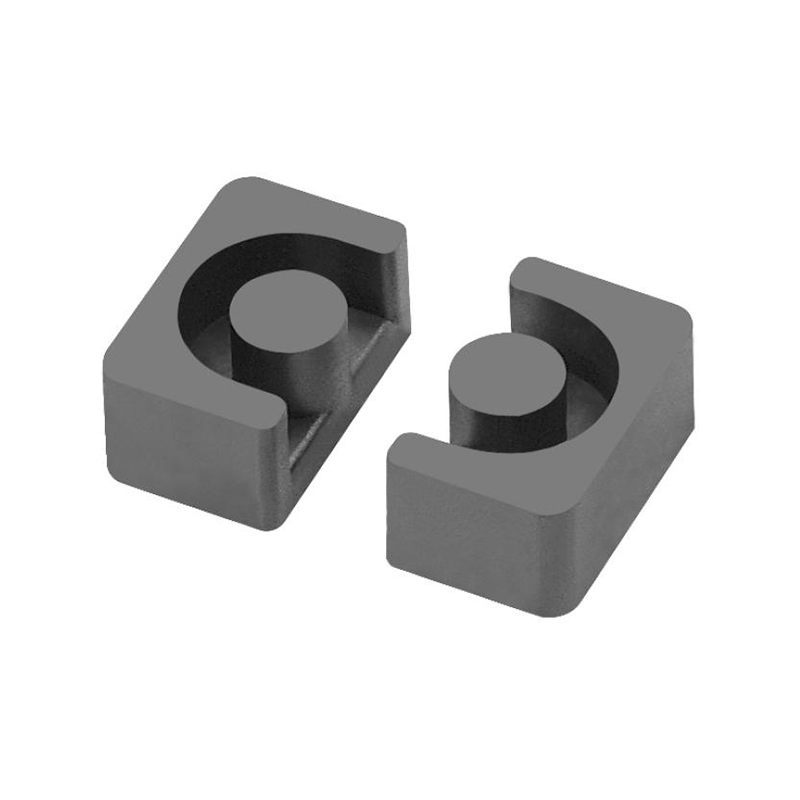
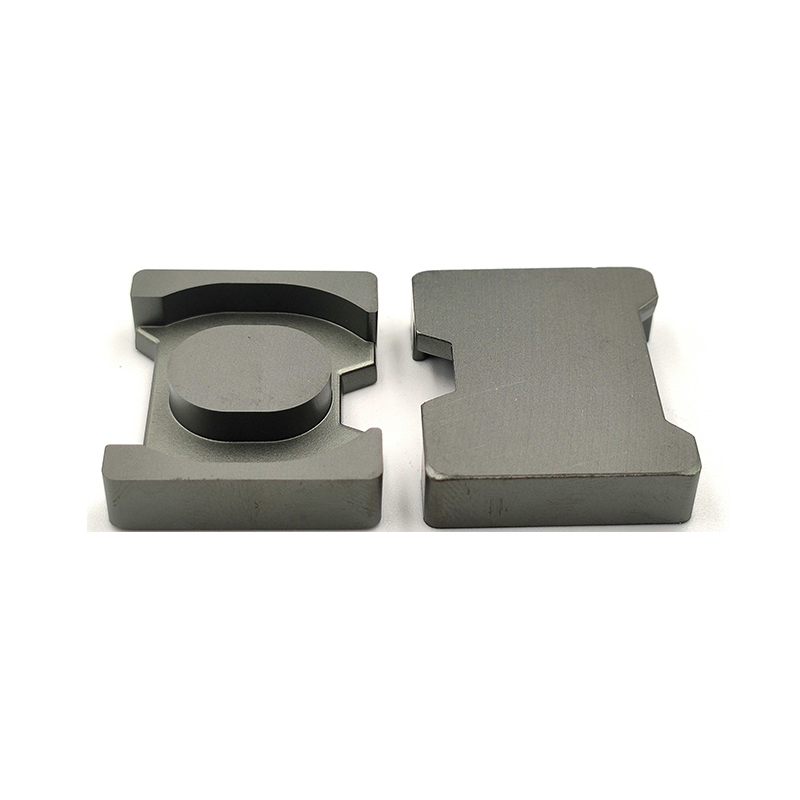
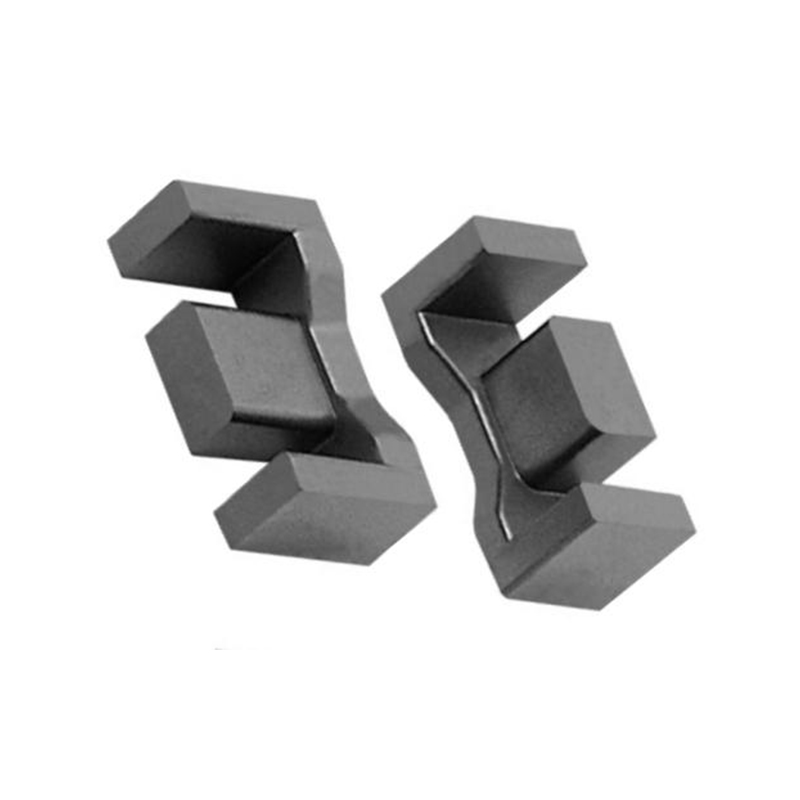
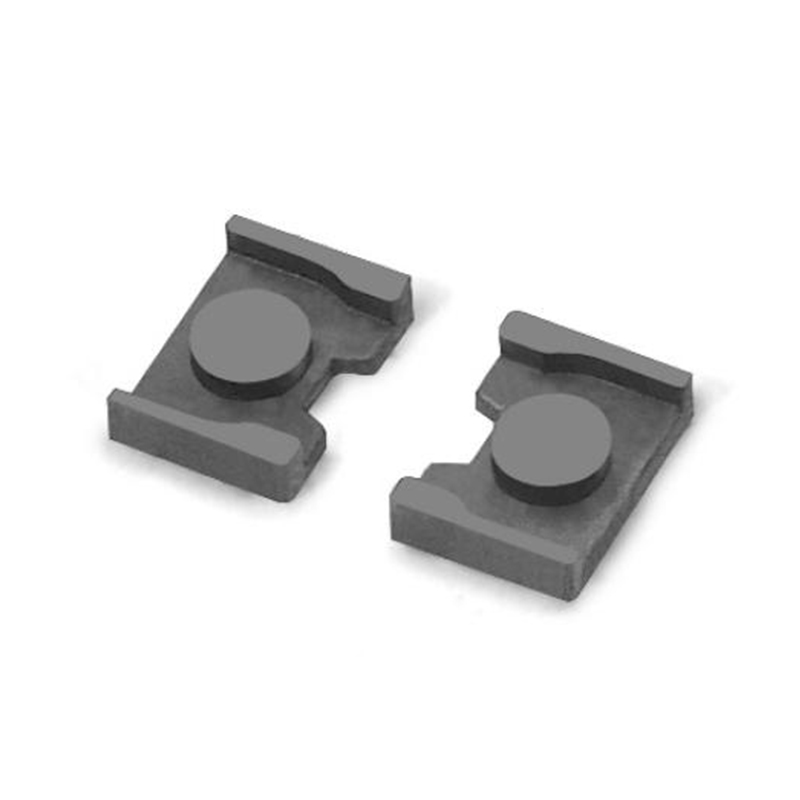
An H-shaped inductor derives its name from its physical structure, resembling the letter “H.” This design consists of a core with two parallel magnetic legs connected by a crossbar, forming an H-like shape. The coil is typically wound around the central limb, optimizing magnetic flux distribution and reducing losses.
Key Features of H-Shaped Inductors
| Feature | Description |
| Core Material | Ferrite, powdered iron, or laminated steel for high permeability and low core losses. |
| Winding Configuration | Concentrated or distributed winding to minimize resistance and parasitic capacitance. |
| Magnetic Flux Path | Closed-loop design reduces leakage flux, improving efficiency. |
| Thermal Performance | Better heat dissipation due to increased surface area. |
Advantages of H-Shaped Inductors
-
High Inductance Density
- The H-shaped core allows for more turns in a compact space, increasing inductance without significantly raising the component size.
-
Reduced Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
- The symmetrical structure minimizes stray magnetic fields, making these inductors suitable for noise-sensitive applications.
-
Improved Thermal Management
- The open design enhances airflow, reducing thermal resistance and preventing overheating in high-current applications.
-
Lower Core Losses
- The optimized magnetic path decreases hysteresis and eddy current losses, improving efficiency in power electronics.
Applications of H-Shaped Inductors
H-shaped inductors are widely used in various industries due to their reliability and performance. Some common applications include:
- Power Supplies – Used in DC-DC converters, voltage regulators, and switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) for energy storage and filtering.
- RF Circuits – Employed in impedance matching, filtering, and signal conditioning due to their stable inductance.
- Automotive Electronics – Found in electric vehicle (EV) power systems, battery management, and onboard chargers.
- Renewable Energy Systems – Utilized in solar inverters and wind turbine converters for efficient energy transfer.
Comparison with Other Inductor Types
| Parameter | H-Shaped Inductor | Toroidal Inductor | Drum Core Inductor |
| Magnetic Flux Leakage | Low | Very Low | Moderate |
| Ease of Winding | Moderate | Difficult | Easy |
| Thermal Performance | Excellent | Good | Moderate |
| Cost | Moderate | High | Low |
Design Considerations for H-Shaped Inductors
When selecting or designing an H-shaped inductor, several factors must be considered:
-
Core Material Selection
- Ferrite cores are ideal for high-frequency applications due to low losses.
- Powdered iron cores offer high saturation levels, suitable for power applications.
-
Winding Techniques
- Litz wire reduces skin effect losses in high-frequency designs.
- Multi-layer winding increases inductance but may introduce parasitic capacitance.
-
Operating Frequency
- Higher frequencies require cores with lower hysteresis losses to maintain efficiency.
-
Current Handling Capacity
- The wire gauge and core size must be chosen based on the expected current to avoid saturation.
Common Challenges and Solutions
-
Core Saturation
- Solution: Use a core material with high saturation flux density or increase the core cross-sectional area.
-
Parasitic Capacitance
- Solution: Optimize winding spacing and use segmented winding techniques.
-
Heat Dissipation
- Solution: Incorporate thermal vias or heat sinks in PCB-mounted designs.
Conclusion
H-shaped inductors offer a balanced combination of high inductance, efficiency, and thermal performance, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. By understanding their design principles and key selection criteria, engineers can optimize their use in power electronics, RF circuits, and renewable energy systems.
Whether you’re designing a high-frequency converter or a robust power supply, the H-shaped inductor provides a reliable solution with minimal trade-offs. Its unique structure ensures better magnetic performance and thermal management, making it a preferred choice in modern electronics.
By incorporating these insights into your projects, you can enhance circuit efficiency and reliability while minimizing electromagnetic interference and power losses.

 中文简体
中文简体